In the quest for a cozy and warm home, the efficiency of your radiators plays a vital role. But have you ever pondered whether old radiators are less efficient than their newer counterparts? It’s a question that lingers in the back of your mind as you search for ways to optimize your heating system. In this article, we will explore the intriguing topic of old versus new radiators, unveiling the truth behind their efficiency and helping you make an informed decision on how to effectively heat your home.
Overview of Radiators
Definition of radiators
Radiators are heating devices used to warm up spaces by transferring heat into the surrounding environment. They typically consist of a metal structure with a series of fins or tubes that help distribute the heat. Radiators commonly use hot water or steam to generate heat, which is then released into the air.
Purpose of radiators
The main purpose of radiators is to provide warmth and comfort during colder months. They play a crucial role in residential and commercial buildings by maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature. Radiators are essential for heating rooms, offices, and other spaces, ensuring a pleasant environment for occupants.
Types of radiators
There are various types of radiators available in the market, each with its own unique design and heating mechanism. The most common types include:
- Conventional Radiators: These are traditional radiators that use water or steam to produce heat. They are typically made of cast iron and have a classic, column-like appearance.
- Panel Radiators: These radiators are more modern in design and consist of multiple panels with grooves or fins. They offer efficient heat distribution and are often made of steel or aluminum.
- Electric Radiators: As the name suggests, electric radiators use electricity as a source of heat. They are standalone units that can be easily installed in any room and are controlled by a thermostat.
- Towel Radiators: These radiators are specifically designed for bathrooms and serve a dual purpose of heating the room and providing a place to hang towels. They come in various styles, such as ladder or rail designs.
Efficiency of Radiators
Factors affecting radiator efficiency
Several factors can impact the overall efficiency of radiators. These include:
- Size of the Radiator: The size of the radiator determines the amount of heat it can produce. Choosing the right-sized radiator for a particular space is crucial to ensure optimal heating efficiency.
- Insulation: Proper insulation in the room or building is essential to retain the heat generated by the radiator. Without adequate insulation, heat loss can occur, resulting in reduced efficiency.
- Temperature Control: The ability to control the temperature of the radiator is important for energy efficiency. Having thermostatic valves or smart controls can help regulate the heat output based on the desired comfort level.
Heat transfer mechanisms
Radiators primarily transfer heat through convection and radiation:
- Convection: Convection is the process of heat transfer through the movement of fluid or air. In the case of radiators, this involves the circulation of hot water or steam through the radiator’s pipes or fins, which then releases heat into the surrounding air.
- Radiation: Radiation occurs when heat is emitted directly from the surface of the radiator into the room without the need for any medium. This is why radiators often feel warm even when not in direct contact with them.
Efficiency ratings
Radiators are often rated based on their efficiency, which indicates how effectively they convert energy into heat. The efficiency rating is typically represented as a percentage, with higher percentages indicating better performance. Manufacturers provide efficiency ratings to help consumers make informed decisions about the radiators they choose.

Advancements in Radiator Technology
Improved heat transfer materials
Advancements in radiator technology have led to the development of more efficient heat transfer materials. Traditional cast iron radiators have been replaced with lightweight materials such as steel and aluminum, which offer better thermal conductivity. These materials allow for quicker heat transfer and provide improved heat distribution throughout the room.
Enhanced design and construction
Modern radiators come in sleek and compact designs that blend seamlessly with contemporary interiors. The construction has also been improved to optimize heat dispersion, resulting in more efficient radiators. The addition of increased surface area, such as fins or panels, maximizes heat transfer and ensures maximum warmth in the room.
Digital and smart features
The integration of digital and smart features in radiators has revolutionized the way we heat our spaces. Many new radiators are equipped with programmable thermostats, allowing users to set customized heating schedules. Smart radiators can be controlled remotely through smartphones or connected to home automation systems, enabling energy-efficient and convenient heating management.
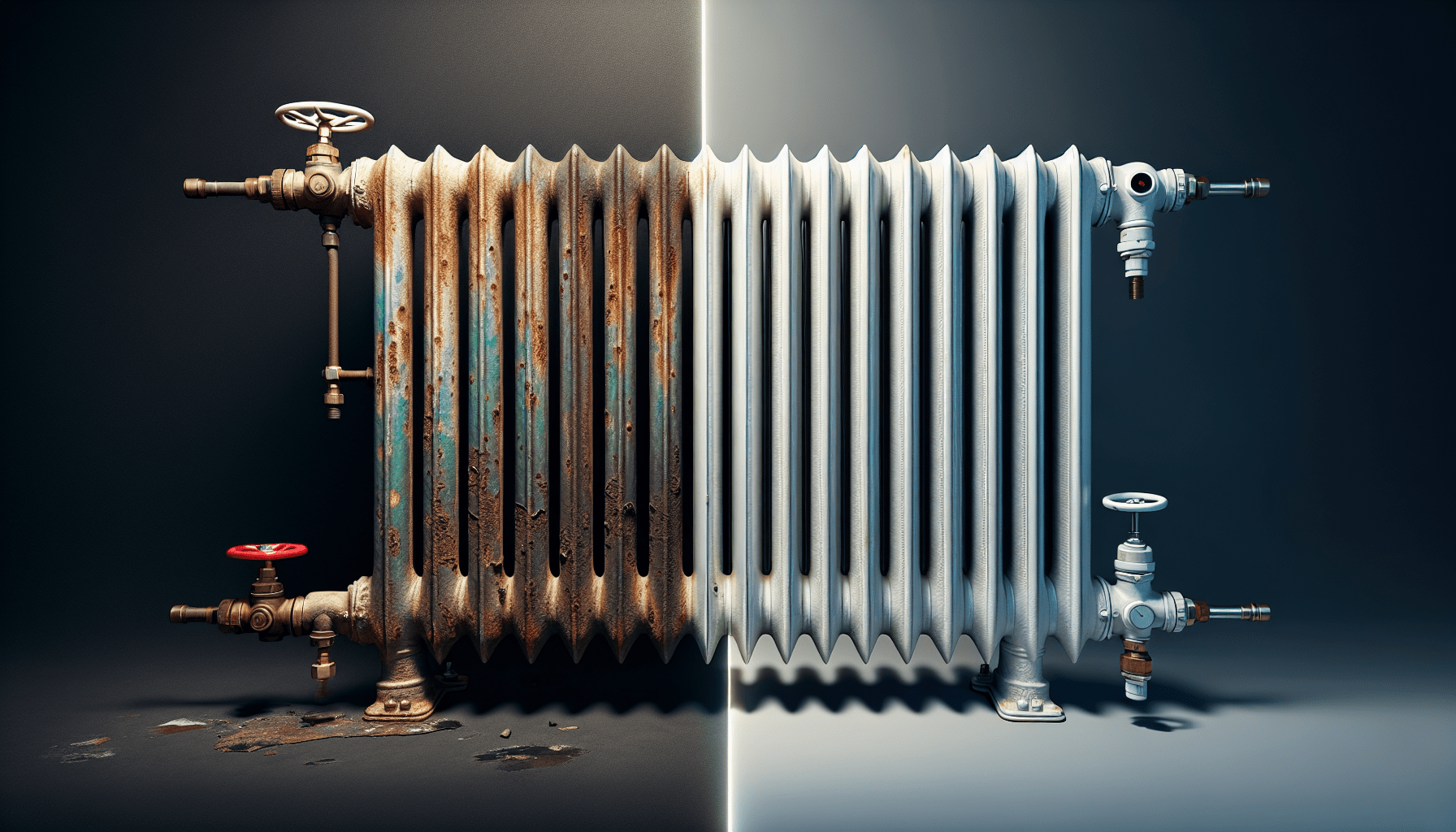
Comparison of Old and New Radiators
Age-related wear and tear
Old radiators, especially those made of cast iron, may suffer from wear and tear over time. Years of continuous use can result in the accumulation of debris, sediment, and sludge within the pipes and fins, reducing their efficiency. These issues are more prevalent in older radiators and can impact their ability to distribute heat effectively.
Corrosion and rust issues
Traditional radiators are susceptible to corrosion and rust, especially if they are not properly maintained or protected. This can lead to leaks and inefficiencies in heat transfer. On the other hand, new radiators are built with corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings, ensuring longevity and optimal performance.
Performance degradation over time
As radiators age, they may experience performance degradation due to factors such as mineral buildup or valve malfunctions. The distribution of heat may become uneven, resulting in certain areas of the room being colder than others. New radiators, with their improved technology and materials, can provide consistent and efficient heat distribution throughout the entire space.

Benefits of New Radiators
Higher energy efficiency
One of the significant benefits of new radiators is their higher energy efficiency compared to older models. Improved heat transfer mechanisms and enhanced design allow new radiators to generate and distribute heat more effectively. This leads to reduced energy consumption and lower heating costs, benefiting both the environment and your wallet.
Improved heat distribution
New radiators are designed to provide more even heat distribution, eliminating cold spots in the room. Whether through the use of fins, panels, or other heat transfer enhancements, these radiators ensure that every corner of the space receives adequate warmth. This results in increased comfort and a more enjoyable living or working environment.
Reduced maintenance
Modern radiators require less maintenance compared to their older counterparts. The use of corrosion-resistant materials and protective coatings minimizes the risk of leaks and rust. Additionally, with the advent of smart radiators, monitoring and adjusting heating settings has become more convenient, reducing the need for manual adjustments and maintenance.
Considerations Before Replacing Old Radiators
Financial implications
Replacing old radiators can involve a significant upfront cost. It is essential to consider your budget and evaluate the long-term financial benefits of investing in new, more efficient radiators. While newer models may result in energy savings over time, the initial investment should align with your financial capacity.
Compatibility with existing heating systems
Before replacing old radiators, it is crucial to ensure compatibility with your existing heating system. Different systems require specific radiator types, such as those connected to a boiler or an electric system. Consulting with a heating professional can help you determine the compatibility and select radiators that work seamlessly with your existing setup.
Installation challenges
Replacing radiators can pose installation challenges, especially if the new radiators have different dimensions or require modifications to the plumbing system. Assessing the feasibility of installation, including any necessary renovations or changes to the pipework, is crucial before making a decision. It may be helpful to consult with a professional plumber to evaluate the installation process and associated costs.

Signs of Inefficient Old Radiators
Uneven heating in rooms
If you notice significant temperature variations in different areas of a room, it may be a sign that your old radiator is not distributing heat efficiently. Cold spots or areas that take longer to warm up indicate that the radiator may need to be replaced or undergo maintenance to restore its optimal efficiency.
Frequent need for bleeding
Old radiators often require regular bleeding to remove air trapped within the system. If you find yourself frequently bleeding your radiator to restore proper heating performance, it may be time to consider replacing it. New radiators are designed to minimize air pockets and provide consistent heat without the need for frequent maintenance.
Excessive noise or hissing
If your radiator emits loud noises or hissing sounds, it may indicate a problem with water flow or trapped air within the system. Over time, old radiators can develop issues that affect their efficiency, leading to noises or hissing. Upgrading to newer radiators can eliminate these issues and provide a quieter and more efficient heating experience.
Calculating Energy Savings
Determining current radiator efficiency
To calculate potential energy savings with new radiators, you first need to determine the efficiency of your current radiator. This can be done by comparing your heating bills to the size of your space and the performance of your old radiator. Energy efficiency professionals can also conduct a thorough assessment, considering factors such as heating patterns, insulation, and heat loss, to provide a more accurate evaluation.
Estimating potential savings with new radiators
Once you have determined the efficiency of your old radiator, you can estimate potential savings with new radiators. Energy-efficient models are designed to optimize heat transfer and minimize energy waste. By comparing the efficiency ratings and calculating the heat output of different radiator options, you can estimate the potential energy savings in terms of reduced heating costs over time.
Consideration of energy costs
When calculating energy savings, it is crucial to consider the current and future energy costs in your area. Energy prices vary, and understanding the rates can help you determine the payback period for your investment in new radiators. By factoring in energy costs, you can make informed decisions about the long-term financial benefits of upgrading to more efficient heating solutions.
Environmental Impact
Energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions
Old, inefficient radiators contribute to higher energy consumption, increasing the demand for fossil fuels and subsequently increasing greenhouse gas emissions. Upgrading to new, energy-efficient radiators can significantly reduce energy consumption, helping to mitigate the environmental impact and lower carbon footprints. By using less energy to heat your space, you contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
Sustainability of new radiator materials
New radiator materials are often chosen for their sustainability and eco-friendly characteristics. Steel and aluminum, which are commonly used in modern radiators, can be recycled, reducing the demand for raw materials and minimizing waste. Additionally, some manufacturers prioritize the use of renewable energy sources during production processes, further minimizing environmental impact.
Long-term environmental benefits
Investing in new radiators not only has immediate energy-saving benefits but also has long-term environmental benefits. As energy-efficient heating solutions become more prevalent, the overall energy demand decreases, resulting in reduced reliance on fossil fuels. This shift towards sustainable heating practices contributes to a cleaner and greener planet for future generations.
Conclusion
Radiators play a crucial role in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures during the colder months. Newer radiators offer numerous advantages over old, less efficient models. With improved heat transfer materials, enhanced design, and digital features, new radiators provide higher energy efficiency, improved heat distribution, and reduced maintenance requirements.
However, before replacing old radiators, it is essential to consider financial implications, compatibility with existing heating systems, and installation challenges. Signs of inefficient old radiators include uneven heating, frequent bleeding requirements, and excessive noise or hissing. Calculating energy savings involves determining the current radiator efficiency, estimating potential savings with new radiators, and considering energy costs.
On top of the energy-saving benefits, new radiators contribute to a healthier environment. They reduce energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and offer sustainable materials that can be recycled. By choosing the right radiator for your needs, you can strike a balance between efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental consciousness. Upgrade to new radiators and enjoy increased comfort, lower energy bills, and a greener future.













